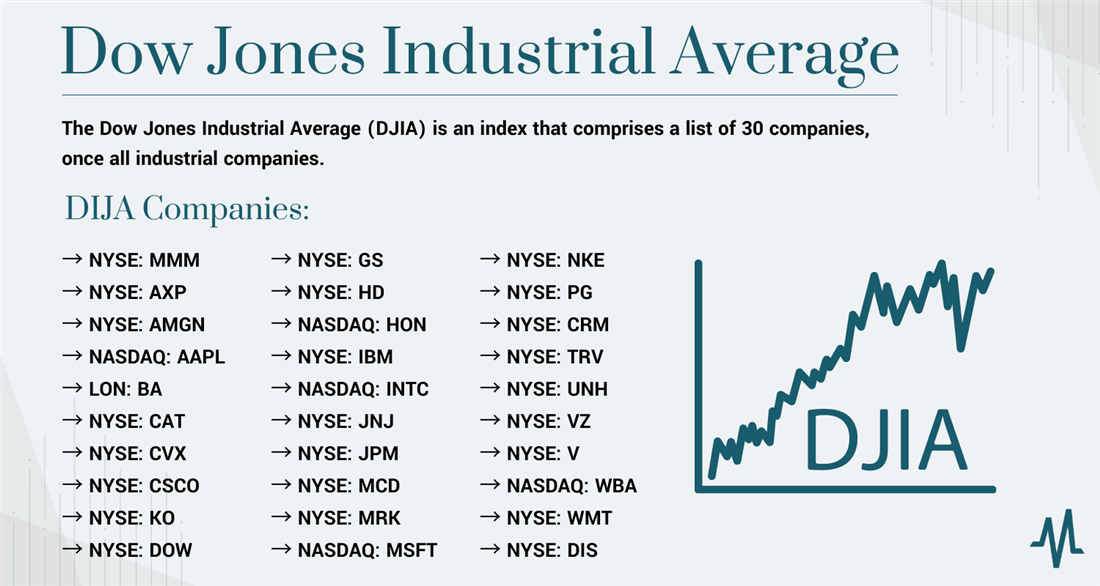
Dow Jones Industrial Average Index (DJIA): Price-Weighted + Dow Divisor
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), commonly referred to as the Dow, is one of the most recognized stock market indices in the world. It represents the performance of 30 large publicly-traded companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq stock exchange.
What sets the DJIA apart from other indices is its unique composition and calculation methodology. Unlike other indices that are market capitalization-weighted, the DJIA is a price-weighted index. This means that the price of each stock included in the index determines its weightage in the overall index value, rather than the company’s market capitalization.
So, how exactly is the DJIA calculated? The index is computed by summing up the prices of all constituent stocks and then dividing the total by a divisor called the “Dow Divisor.” The divisor is adjusted periodically to account for changes such as stock splits, spin-offs, or changes to the index composition.
Originally, when the DJIA was first introduced in 1896, it had only 12 component stocks. Over time, the number of constituents has increased to 30, providing a broader representation of various sectors of the U.S. economy. The selection of these 30 companies is done by the editors of The Wall Street Journal, which owns the index.
The DJIA includes some of the most well-known and influential companies across a range of industries. Some of the current components are Apple Inc., Microsoft Corporation, The Walt Disney Company, Goldman Sachs Group Inc., and many others.
It is important to note that due to its price-weighted nature, higher-priced stocks have a greater impact on the DJIA’s movements compared to lower-priced stocks, regardless of their respective market capitalizations. This means that a large percentage move in a high-priced stock can have a significant effect on the overall index value.
The DJIA is widely tracked and used as a benchmark to gauge the overall performance of the U.S. stock market. Investors and market participants closely monitor its movements to assess the health of the economy and make informed investment decisions.
In conclusion, the Dow Jones Industrial Average Index (DJIA) is a price-weighted index consisting of 30 major U.S. companies. Its unique calculation methodology, which involves summing up the prices of constituent stocks and dividing by a divisor, sets it apart from other market indices. The DJIA serves as an important indicator of the overall performance of the U.S. stock market and influences investor sentiment around the world.